Australia's Extreme Heat
Australia's extreme heat, Feb. 7-14, 2017 (credit: Climate Signals)
Over the past few years, Australia has experienced some of its worst heatwaves according to research published in Geophysical Research Letters. According to a study conducted by researchers at the Australian National University (ANU), metropolitan areas of Melbourne and Sydney should begin to prepare for extreme temperatures that could exceed 50C (~122F) during future summers.
The investigators determined that:
"extreme temperatures affect ecosystems, infrastructure, and human health. Understanding how climate change is impacting weather extremes and how this will change under future global warming are important scientific questions. Previous studies have focused on how current temperature extremes have been impacted by climate change. We took a different approach and examined how severity of temperature extremes may change in the future."
In the study, the range of temperature severity was considered under warming limits set as goals in the Paris climate agreement, 1.5C (2.7 degrees Fahrenheit) and 2C (3.6F), of global warming. The ANU study found the magnitude of future temperatures for Australia does not necessarily increase at the same rate as global warming. The analysis determined daily temperature extremes of 3.8C may occur for Australian states above existing records, even under the most ambitious goals set in Paris to limit global warming.
For a perspective on temperature severity impact, a chart has been developed by Carbon Brief to compare the impacts of 1.5C and 2C on environment and natural resources in Australia.
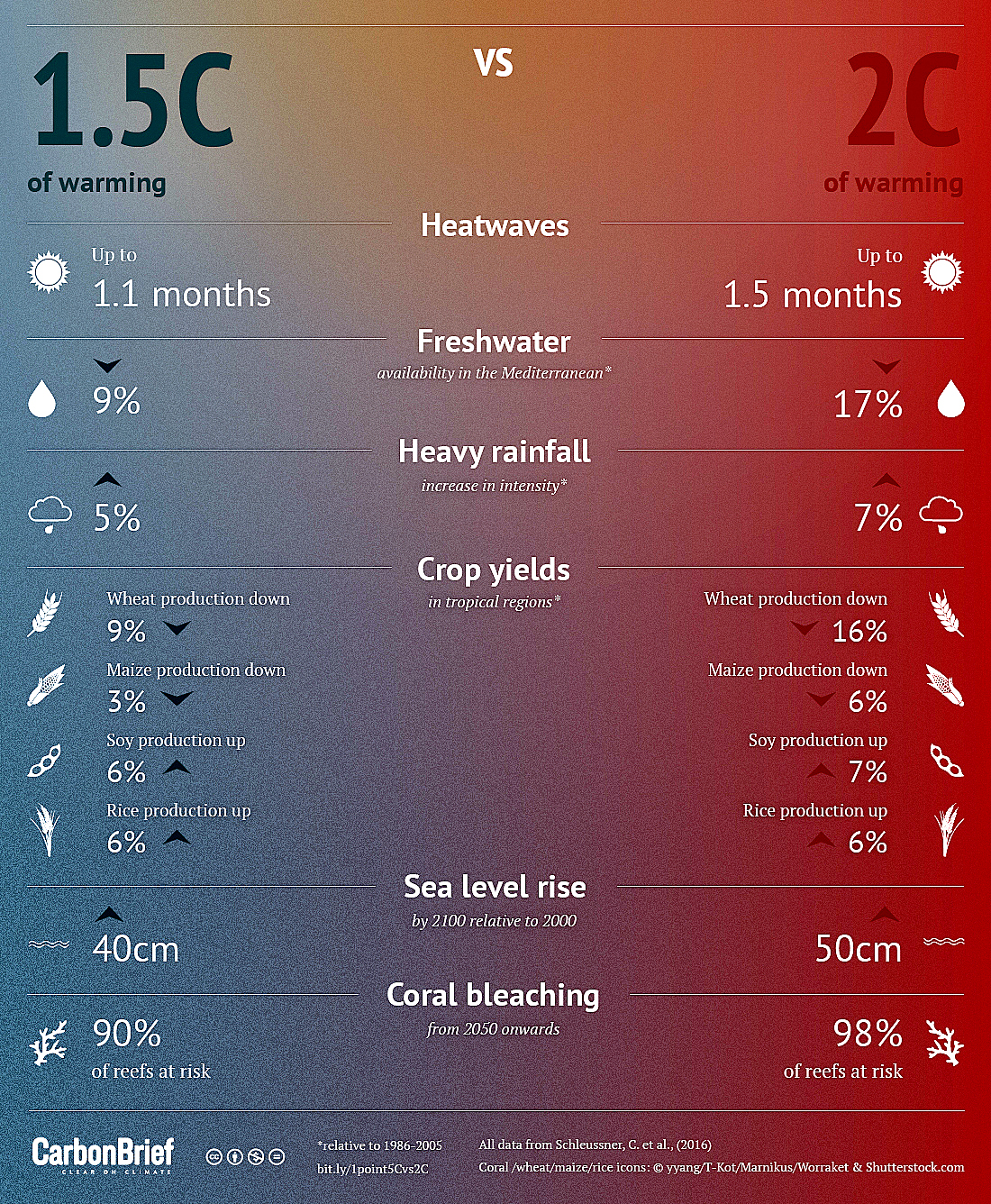
Temperature Comparison of Climate Impacts,1.5C & 2C (credit: Carbon Brief)
For an example, a policeman fried an egg on the hood of his car during one Australian heatwave.
The ANU researchers concluded:
"the possible severity of future temperature extremes will pose serious challenges to general preparedness for future climatic change in Australia".
WHB