Climate Change Tutorials
Aspects of climate science and the impacts from increased greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere are explained in high school textbooks. Two examples from basic chemistry and biology:
Chemistry 101: The reaction of carbon dioxide (CO2) gas if dissolved in water (H2O) creates carbonic acid (H2CO3). The chemical formula for the process is: CO2 + H2O → H2CO3
The European Space Agency used their SMOS Earth Explorer satellite to gather 'big data' measurements of ocean pH levels from space. Until now, this basic water chemistry was only available from samples taken by ships and determined by lab experiments. One of the leaders of the ESA efforts noted: "by capitalizing on salinity measurements from SMOS, we can generate novel, value-added, data products to produce a global surface ocean pH atlas". The ESA's determinations show how the ocean's chemistry is changing and is becoming more acidity.
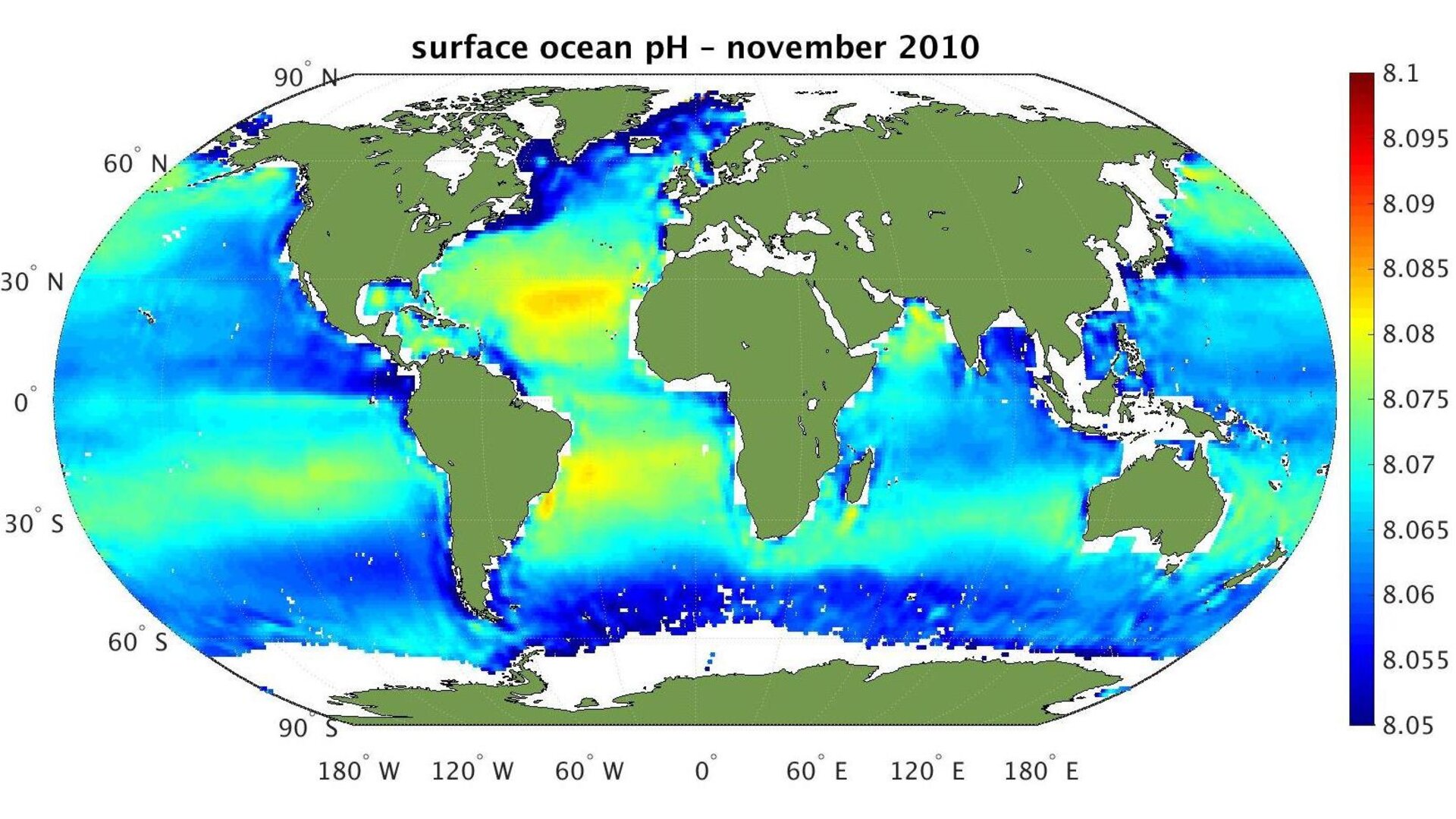
Ocean acidity map (credit: European Space Agency, SMOS satellite)
The researchers published their results in Environmental Science & Technology with maps being available to other oceanic and marine biology investigators. Their abstract notes: "Approximately a quarter of the carbon dioxide emitted into the atmosphere is absorbed by the oceans. This oceanic uptake leads to a change in marine carbonate chemistry resulting in a decrease of seawater pH and carbonate ion concentration, a process commonly called: Ocean Acidification”.
Biology 101: The formula of the effect of carbonic acid on calcium carbonate (CaCO3), the structural material of many marine organisms is: CaCO3 + H2CO3 → Ca + 2HCO3
This is a fundamental biological issue relating to this formula which produces dissolved calcium. A significant number of marine organisms rely on calcium carbonate for their hard exoskeletons. Marine micro-organisms including photosynthetic diatoms and algae produce upwards of 70% of the Earth's oxygen; the symbiotic associations of bacteria and animals (polyps) produce the world's coral reefs; and shellfish including clams, mussels, and oysters as well as lobsters and crabs all require calcium carbonate to build their hard structures. These two inter-related facts of chemistry affecting biology is made clear by Nature Magazine.
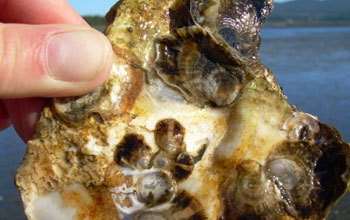
Deformed oyster shells in Oregon hatchery (credit: NSF)
The process of connecting the atmosphere to ocean chemistry is cleverly illustrated by an animation.
The Nature study highlights impacts on the commercial marine shellfish industry from declining harvests with deformed, weak shells due to ocean acidification. These climate change impacts are happening now. Production of oysters and clams produced by aquaculture, combined with crab and lobster harvests, represent an industry exceeding $1 billion supplying these shellfish to restaurants and fresh markets. One of the authors said:“Ocean acidification has already cost the oyster industry in the Pacific Northwest nearly $110 million and jeopardized about 3,200 jobs.”
Losses to seafood lovers aside, the research didn't determine valuations for environmental services provided by oysters beds to purify water or reduce the destructive forces of coast storm surges.
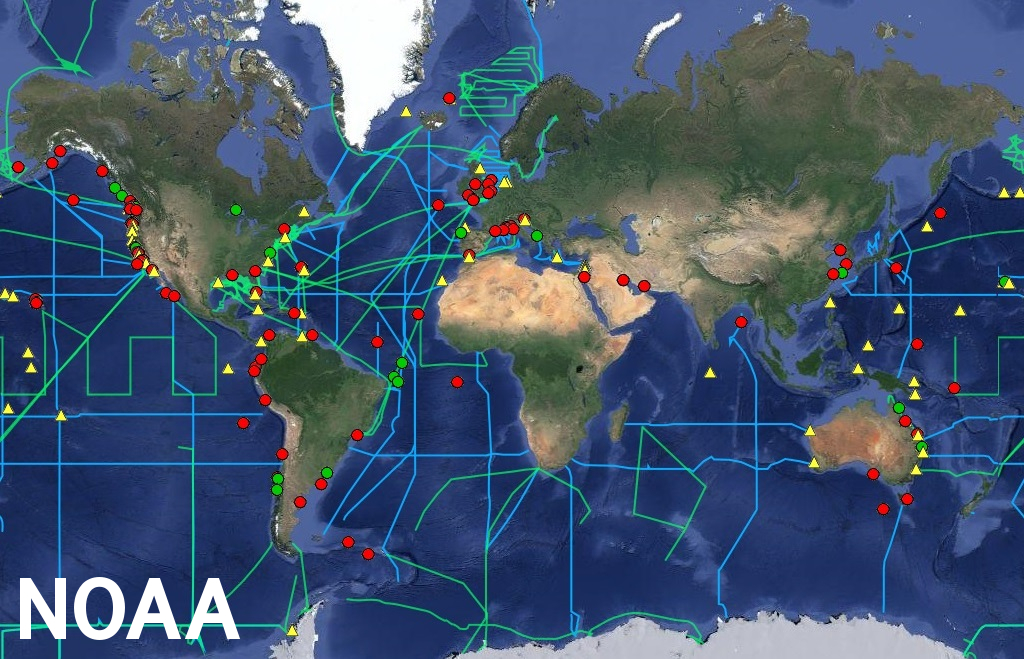
Coastal locations most affected by ocean acidification, red dots (credit: NOAA)
So, when you order your next bucket of steamers, a plate of shucked oysters, or a lobster tail and the bill is sky-high, remember your high school chemistry and biology tutorials. WHB